
Image property of IHREC
42(2)(a) of the IHREC Act 2014 requires an organisation to set out in its strategic plan “an assessment of the human rights and equality issues it believes to be relevant to the functions and purpose of the body and the policies, plans and actions in place or proposed to be put in place to address those issues”.
Section 42 of the Irish Human Rights and Equality Act 2014 imposes a statutory obligation on public bodies in performing their functions to have regard to the need to:
- eliminate discrimination
- promote equality of opportunity and treatment for staff and persons to whom it
provides services and
- protect the human rights of staff and services users.
The Public Sector Equality and Human Rights Duty places equality and human rights at the heart of how a public body fulfils its purpose and delivers on its strategic plan.
What Does a Public Body have to Do?
To meet the core requirements of the Duty, a Public Body must Assess, Address and Report.
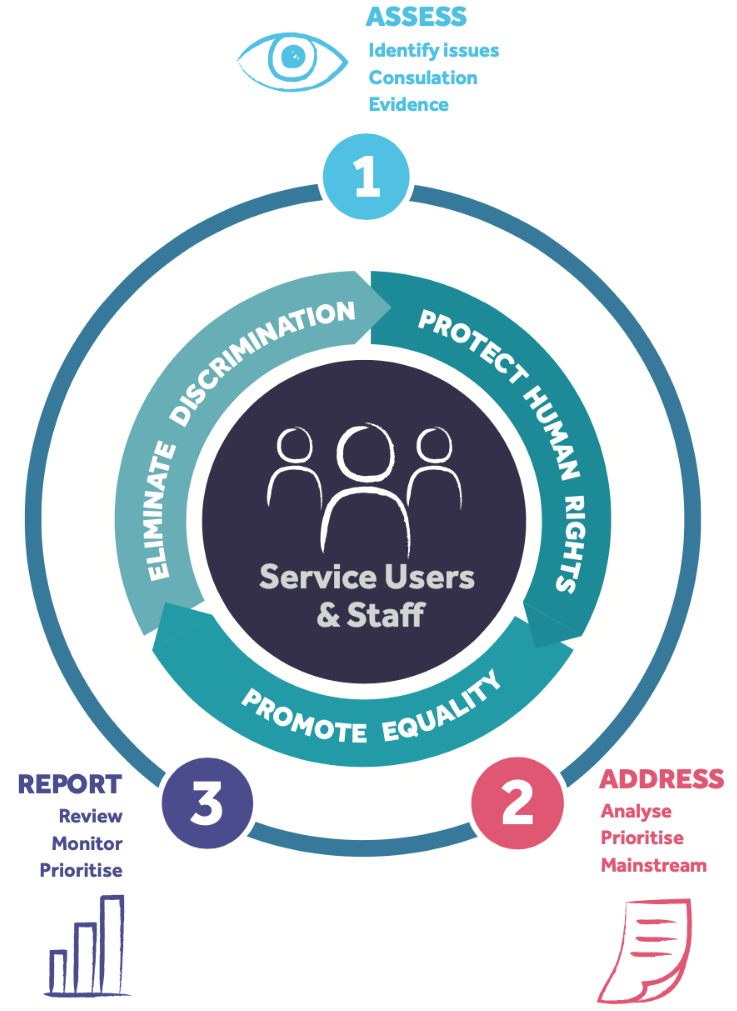
Image property of IHREC
-
ASSESS
Set out in its strategic plan or corporate plan the equality and human rights issues relevant to their work.
This assessment must be based on evidence such as research, government policies (e.g. national strategy for women and girls, national Traveller and Roma inclusion Strategy), consultation with staff and service users.
-
ADDRESS
Set out in its strategic plan the policies, plans and actions that they have or will put in place to address those issues, in a way that is transparent and accessible to the public.
This includes positive actions to bring people to a level playing field.
-
REPORT
A public body is required to report annually on developments and achievements in regard to the equality and human rights issues and actions, in a manner accessible to the public, in its annual report.
These requirements are considered having regard to the public body’s functions, purpose, size and resources available to it.
The obligation to integrate the Duty in a public body’s strategic plan and annual report means that assessing and addressing equality and human rights issues is an ongoing process that should be reviewed and developed in accordance with strategic planning cycles.
What parts of an organisations work are covered?
The Duty applies across all the functions of the organisation:
- Organisational Planning / Corporate Services (strategic planning, budget allocation, procurement, grant funding)
- Human Resources (recruitment, HR policies and practices, staff capacity building)
- Service Provision (delivery of a service or engagement with key stakeholders)
- Research and Policy
- Regulatory & Oversight Functions
Assisting the Effective Implementation of the Public Sector Equality and Human Rights Duty
Tool for an Evidence Based Assessment
Stages for conducting a Human Rights and Equality Assessment
There are three stages to consider when undertaking the Human Rights and Equality Assessment which involve:
- Identifying human rights and equality issues
- Identifying structures and initiatives in place to support human rights and equality
- Prioritising areas for action

The assessment process involves a series of steps as follows:
- Leadership and Responsibility
- Gather Evidence for the Assessment
- Assess and Prioritise the relevant Equality and Human Rights Issues
- Validate and Approve the Final Draft
- Publish and Communicate the Assessment of Equality and Human Rights Issues
Evidence Based Assessment
Examples of External Sources of Information
- Consultation with staff and service users
- Data from Central Statistics Office
- Reports and research from Economic and Social Research Institute (ESRI) and the Commission
- Cases taken to Workplace Relations Commission under employment equality and equal status legislation
- Civil society organisations reports / submissions
Examples of Internal Sources of Information
- Organisation evaluations
- Staff and customer surveys
- Risk management register
- Complaints received
- Research and other commissioned reports





